Seagate Hard disks of 3 Terabyte volume used to be very attractive HDDs (storage) option when they were launched on the market.
Many people and sysadmins have already bought such ones and some sysadmins and company customers that already choose Seagate are badly suffering because of that and thus it is good to warn others to stay away from 3TB SeaGate Hard Disks.
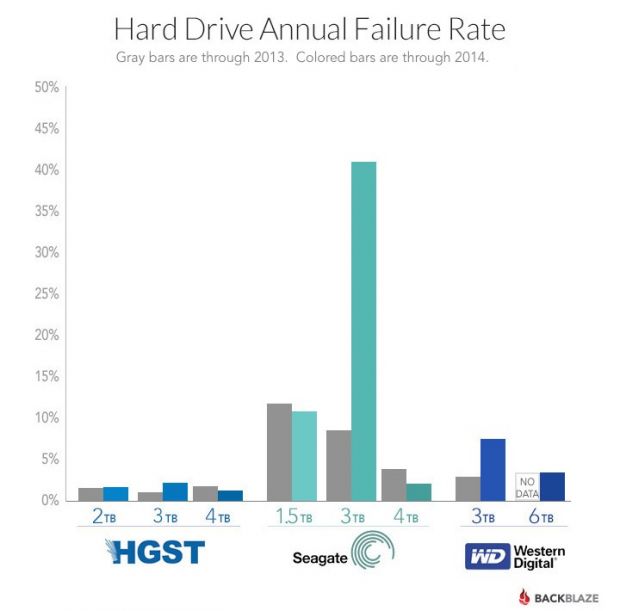
Backblaze (Online Backup) company is one of the most severely affected companies that made the choise to use Seagate as a storage devices on their Cloud inter-connected servers. They used 41 213 hard disks in their computing Data Center as of 31 December 2014.
In their disk arrays they have used Western Digital (now part of Western DIgital) and of course pitily Seagate.
The problematic hard disks that they faced issues with are Seagate Barracuda 7200.14 3TB sized is the hard disks with most failures within Backblaze for whole 2014 about 40% percents!! of all 3TB hard disks the company had break up, died or had to be replaced because of I/O disk failures and bad-sectors.
It is not exactly clear what is the reason for such a high failures but Seagate were leaders in failures followed by Western Digital and HGTX (the ex-Hitachi).
Just for a comparison Backblaze reports that 4 Tetabyte hard disks which they bought last year had failures, very rarely and in general the company is quite happy with Seagate / WD disks of 4 TB volume.
Seagate Barracuda 7200.14 3TB disk drives mounted on their servers are the one who had most hardware issues and the company recommends anyone willing to buy a new HDD to stay away from this volume.
Western Digitals 3TB HDDs had 10% of failure rate, HGTS had only 2.6% and Seagate exact failed HDDs were approximately 43.1% with a HDD failure!!
No severe hardware HDD failures are reported with 4 TB hdds.
4TB Seagate HDDs gave 5% of defects, followed by WD with 3-4% and HGTS with only 1.4%.
Statistics clearly shows it if you want to buy a big storage for your big data / Web / FTP / Dropbox (Cloud) hosting Company as of time of writting 26.01.2015 it is better equip your Big Storage Array racks with HGTS branded hard drives.